期货交易成本英文(期货市场交易成本)
Understanding Futures Trading Costs
Futures trading involves various costs that traders should understand before engaging in this financial market. These costs include fees, commissions, margin requirements, and potential slippage. Knowing how these costs affect trading can help traders manage their risk and optimize their returns.
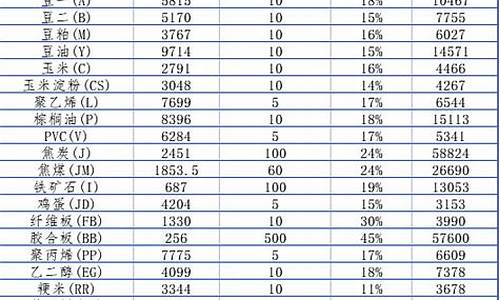
1. Fees and Commissions
One of the primary costs of futures trading is fees and commissions charged by brokers. These fees can vary depending on the broker and the type of futures contract traded. Traders should carefully consider these costs when choosing a broker and factor them into their trading strategy.
2. Margin Requirements
Another significant cost of futures trading is margin requirements. Futures contracts are highly leveraged instruments, meaning traders can control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. However, this leverage comes with the requirement to maintain a margin balance with the broker, which can tie up capital and increase trading costs.
3. Slippage
Slippage occurs when the price at which a trade is executed differs from the expected price. This can happen due to market volatility, liquidity issues, or delays in order execution. Traders should be aware of slippage and consider it when calculating the potential costs of their trades.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the costs associated with futures trading is essential for traders to make informed decisions and manage their risk effectively. By considering fees, commissions, margin requirements, and slippage, traders can develop a comprehensive trading plan that maximizes their chances of success in the futures market.




